SPF in Office 365 is checked using default policies, but messages are not blocked by default. If we want to block delivery of messages, that do not meet the SPF criteria, we can do this by changing the default settings.
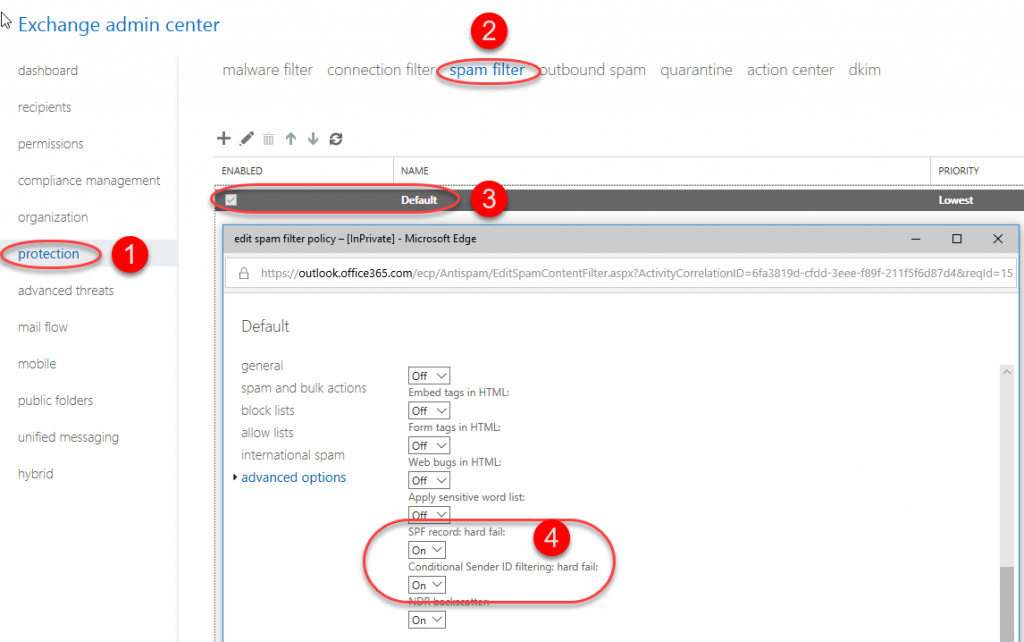
When we change the SPF monitoring settings, Office 365 will deliver all e-mail, that does not meet the criteria, to quarantene. From there, users or admins can release it. By default, e-mails stay in quarantene for 15 days.
If we want to accept messages even if they don’t meet the SPF policies, we can add the IP address of the mail server, that is sending those e-mails, to the list of safe IP addresses.

Using the Mail Flow, we can set Office 365 to accept an email, that does not meet SPF criteria and has delivered it to quarantene.
This can be set up based on the e-mail header, where we check “Authentication-Results” where the result is “spf=fail”.

We can also set up what information Office 365 should include when notifying us about receiving an e-mail, that doesn’t meet SPF criteria. We can even select to include the entire message, which includes the message header, which can be very useful when determining the origin of the message and what SPF settings are causing problems.

The screenshot below is an example of a message we receive from Office 365.
